Bone Marrow Concentration & Stem cells
WHAT IS BONE MARROW?
Bone marrow is the soft spongy tissue that is found in the center of your bones. In adults, marrow in the large bones are the producing center of your red blood cells, white blood cells and plasma components. Since this is the location of production, immature forms of these cells called stem cells, will be found here.
WHAT ARE BONE MARROW STEM CELLS?
The immature stem cells found inside the bone marrow have the potential to develop into various mature cells such as muscle cell, the cells of a vessel, cells of a cartilage or even bone cells. Two of the main stem cells found in bone marrow include:
- Hematopoietic stem cells – give rise to the three classes of blood cells that are found in circulation: white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. These are the cells that actually drive tissue regeneration and create supportive circulation.
- Mesenchymal stem cells – also known as Marrow Stromal Cells. These cells have the capacity to form osteoblasts or bone structure, chondrocytes or cartilage, and myocytes or muscles.
IS THE PROCESS EXPERIMENTAL OR NEW?
Bone marrow extractions have been accepted and are used in fields such as oncology and hematology. The vital components in bone marrow were initially used for transplant purposes in patients with an immune deficiency, such as caused by blood cancers or disorders. The skill of extracting has not changed but the donor is YOU and the recipient is YOU preventing any rejection or allergic reactions.
ARE THERE ANY RISKS?
Bone marrow extractions are safe procedures when conducted by a trained professional in a sterile environment. Complications are rare but can include:
• Bleeding, particularly in patients with low platelet count or clotting disorder.
• Infection, in patients with weakened immune systems. Antibiotics are given post extraction to prevent infection.
WHAT TO EXPECT?
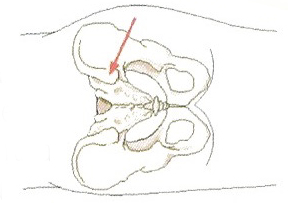
The area of extraction is locally numbed so pain is minimal. Bone marrow is extracted from the back of the patient’s pelvis or hipbone from an area called the posterior iliac crest. A suctioned syringe attached to a long needle is used to reach the posterior aspect of the hip, during which minimal discomfort is felt due to local anesthetic.
The collected sample is transferred through a filter then placed into a centrifuge. Spinning at high-speed separates the platelets and stem cells from the bone marrow sample. This concentration of stem cells and healing components, collectively known as the bone marrow concentrate are reintroduced to the injured area.
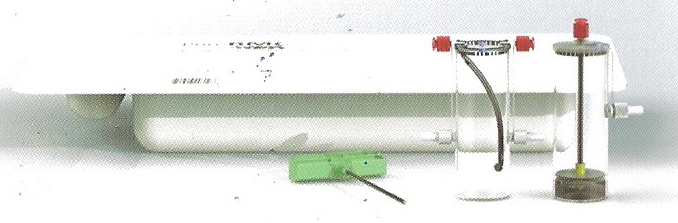
HOW LONG IS THE PROCEDURE?
Treatment is in an outpatient setting. The actual extraction can take up to 10 minutes, but the concentrating process may take up to one hour, during which the patient will be waiting.
HOW LONG IS RECOVERY TIME?
The majority of patients are able to return to usual activities within 1 to 2 days but some pain maybe felt for up to one week.
WHAT SHOULD I DO OR NOT DO?
Prior to your procedure, you should drink plenty of fluids and eat a good meal. Please consult with your physician about medications or prior history of blood disorders. Pain control will be given if needed.
THE HEALING PROCESS
Bone marrow stem cells are the regenerative cells responsible for repair and rebuilding damaged tissue. The concentrated cells accelerate the healing process, promote strength, offer pain relief and improve overall function. The healing cascae can be active and take place over 4-6 weeks. A follow-up PRP procedure may be recommended if desired relief is not met.